Hepatitis C is the liver-based viral infection that is caused by the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). It is a significant health issue in the world since most infected individuals do not exhibit the symptoms over years and enable the disease to silently destroy the liver in the long run.
| Aspect | Details |
| Disease Name | Hepatitis C |
| Cause | Hepatitis C virus (HCV) |
| Affected Organ | Liver |
| Type of Disease | Viral infection (can be acute or chronic) |
| Mode of Transmission | Contact with infected blood (unsafe injections, blood transfusion, shared needles, unsterilized medical equipment) |
| Not Spread By | Casual contact, food, water, hugging, kissing |
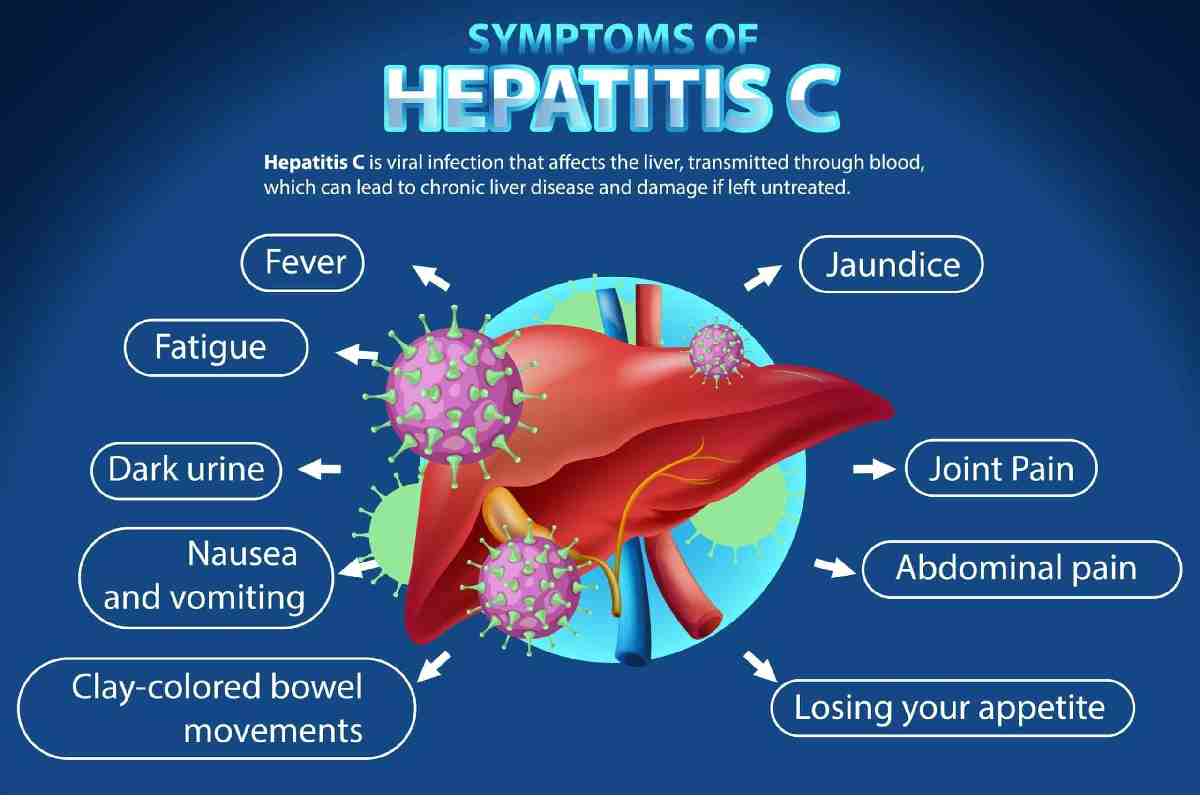
| Symptoms | Fatigue, nausea, jaundice, dark urine, abdominal pain (many people have no symptoms) |
| Acute Hepatitis C | Short-term infection occurring within 6 months of exposure |
| Chronic Hepatitis C | Long-term infection that can last for years and damage the liver |
| Complications | Liver cirrhosis, liver failure, liver cancer |
| Diagnosis | Blood tests (HCV antibody test, HCV RNA test) |
| Treatment | Antiviral medications (Direct-Acting Antivirals – DAAs) |
| Cure Rate | Over 95% with proper treatment |
| Vaccine Availability | No vaccine available |
| Prevention | Safe injections, screened blood, avoid sharing needles or razors |
| Risk Groups | IV drug users, healthcare workers, dialysis patients |
| Global Impact | Millions affected worldwide |
Table of Contents
Hepatitis C Self-Care: Self-care Guide.
Hepatitis C is a liver infection or hepatitis virus, which is a medically treated condition, but self-management plays a major role in the maintenance of liver disorders and quality life. Through proper discipline in the normal activities of day to day life, most people with hepatitis C can still live an active and healthy life.
One of the self-care measures that should be taken is avoiding alcohol. Another burden on the liver is caused by alcohol and can hasten the destruction of the liver. Small doses should be avoided except when prescribed by the doctor. Proper balanced nutritious diet is also crucial.
The intake of fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is good in the functionality of liver, and the immunity, in general.
Light to medium exercise such as walking or yoga may contribute to the reduction of fatigue and good body weight. However, do not work too hard, you should listen to your organism.
A proper rest and sleep will aid in controlling some of the hepatitis C symptoms such as fatigue and weakness.
Drugs and supplements are also important to be sensitive. Other drug could harm the liver like over the counter painkiller and the herbal products. Do not self-prescribe anything. Infection control measures such as sharing of razors, toothbrushes, needles and so on will reduce the virus spread to other people.
Finally, there is emotional well-being. It may be of great help when an individual is forced to live with a chronic condition using stress management, counseling, or even support groups. Regular checkups and prescription regimes contribute towards the attainment of better long term outcomes. The management of hepatitis C can be achieved by regular medication and self-care.
| Self-Care Area | What to Do | Why It Helps |
| Alcohol Intake | Completely avoid alcohol | Prevents further liver damage |
| Diet | Eat fruits, vegetables, lean protein | Supports liver health |
| Exercise | Light to moderate physical activity | Boosts energy and immunity |
| Medication Safety | Consult doctor before medicines | Avoids liver toxicity |
| Rest & Sleep | Get enough daily rest | Reduces fatigue |
| Infection Control | Don’t share personal items | Prevents virus spread |
| Mental Health | Manage stress, seek support | Improves emotional well-being |
Types of Hepatitis C
| Type of Hepatitis C | Description | Duration | Key Points |
| Acute Hepatitis C | Short-term infection occurring soon after exposure to the virus | Up to 6 months | Often asymptomatic; some people clear the virus naturally |
| Chronic Hepatitis C | Long-term infection when the virus remains in the body | More than 6 months | Can lead to liver damage if untreated |
| Resolved Hepatitis C | Infection cleared naturally or after treatment | Permanent clearance | No active virus, but antibodies remain |
| Relapsed Hepatitis C | Virus returns after initial response to treatment | Varies | Requires further medical evaluation |
| Reinfected Hepatitis C | New infection after being cured | New exposure | Possible if exposed again to infected blood |
Symptoms of Diseases
Hepatitis C can go from a mild disease enduring half a month to a severe and ongoing medical issue.
Individuals, particularly at the intense stage, can have hepatitis C without any side effects, and may not realise they have. In addition, it makes it simpler to communicate with other people.
| Stage | Common Symptoms | Explanation |
| Early / Acute Stage | Fatigue, mild fever, nausea | Often mild or mistaken for flu |
| Loss of appetite | Due to liver inflammation | |
| Muscle or joint pain | Common viral response | |
| Abdominal discomfort | Pain or heaviness on right side | |
| Chronic Stage | Persistent fatigue | Most common long-term symptom |
| Nausea and indigestion | Ongoing liver stress | |
| Mild jaundice | Yellowing of skin and eyes | |
| Brain fog | Difficulty concentrating | |
| Advanced Liver Disease | Severe jaundice | Indicates significant liver damage |
| Dark urine | Excess bilirubin in blood | |
| Pale stools | Reduced bile production | |
| Abdominal swelling (ascites) | Fluid buildup due to cirrhosis | |
| Easy bruising or bleeding | Poor clotting factor production | |
| Swollen legs | Fluid retention | |
| Weight loss | Poor nutrient processing | |
| Severe Complications | Confusion or drowsiness | Hepatic encephalopathy |
| Vomiting blood | Bleeding from esophageal varices | |
| Severe weakness | Liver failure sign |
Intense hepatitis C symptoms
The vast majority with intense hepatitis C don’t foster side effects. However, on the off chance that they do, side effects typically emerge between 2 and 12 weeks of trusted Source after openness.
Individuals seldom get a finding of intense hepatitis C as it needs authoritative side effects. Along these lines, specialists frequently call hepatitis C the quiet scourge.
The intense side effects are the same as other viral contaminations. Side effects of extreme hepatitis C include:
- a fever
- fatigue
- abdominal pain
- loss of appetite
- nausea or vomiting
- dark urine
- clay-coloured stool
- joint pain
- jaundice, rarely
However, As specified by the CDC, close to half rusted Source of individuals with intense hepatitis C clear the infection from bodies without therapy and don’t temporary the persistent condition; scientists don’t know why this happens to specific individuals and not others.
Persistent hepatitis C
Hepatitis C becomes persistent when the body can’t clear the infection. By and large, ongoing hepatitis C causes no side effects or causes general side effects, like constant weariness or
wretchedness. An individual may figure out they have the condition during a normal blood test or evaluation for a blood gift.
Early determination and treatment can forestall liver harm. Left untreated, persistent hepatitis C can prompt:
- CHRONIC liver sickness, which can happen gradually north of quite a few years with next to no side effects
- cirrhosis, or liver scarring
- liver disappointment
- liver malignant growth
Causes and risk factors of hepatitis C symptoms
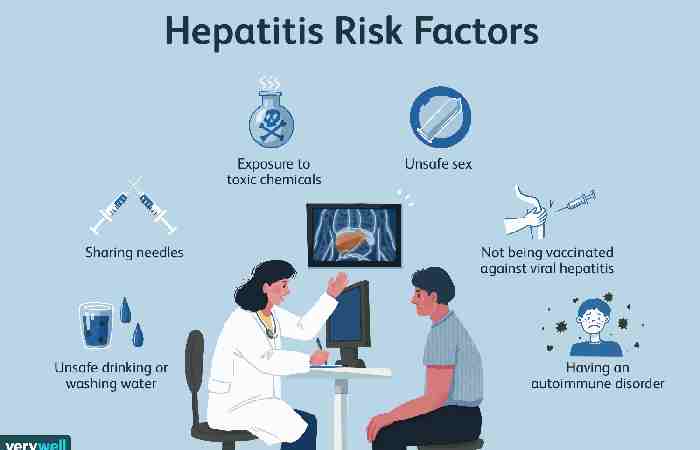
HCV causes hepatitis C. Individuals contract the infection through blood-to-blood contact with sullied blood. For transmission to happen, blood containing HCV should enter an individual’s body without HCV.
A bit of blood, invisible to the unaided eye, can convey many hepatitis C infection particles, and the infection isn’t difficult to kill.
The CDC Trusted Source reports the accompanying gamble factors for creating hepatitis C:
- utilizing or having utilized injectable medications, the most widely recognized course in the U.S.
- getting bondings or organ transfers before 1992, which is before blood screening opened up
- having an openness to a needle stick, which is most regular in individuals who work in medical services
- being brought into the world to a mother who has hepatitis C
The CDC offers counsel by Trusted Source on cleaning needles on the off chance that utilizing spotless and sterile ones is preposterous. Although detergent can kill HCV in hands, it might not affect other gear. Bubbling, consuming and using liquor, peroxide, or other normal cleaning liquids to wash hardware can decrease the amount of HCV. Yet, it probably won’t prevent an individual from getting the disease.
An individual can’t get the infection from easygoing contact, breathing, kissing, or sharing food. There is no proof that mosquito chomps can move the disease. The gamble is low. However, individuals can likewise contract hepatitis C by:
- sharing things that could have contact with blood, like toothbrushes or razors
- having intrusive medical care methodology, like infusions
- getting a tattoo from an unregulated supplier
Because of these variables, persons in danger can have screening to preclude HCV.
Is it curable, and Is it contagious?
Yes. Present-day medicines can fix hepatitis C, as a rule. These medicines include a blend of antiviral meds taken for 8-24 weeks Trusted Source.
One way or another, since a lot of those who are infected with HIV do not know that they are infected, this makes them take long before seeking testing and treatment.
Yes, the hepatitis C is contagious. HIV is contracted by humans when they are exposed to infected blood through a blood-to-blood contact.
Treatment
| Treatment Aspect | Details |
| Main Treatment | Direct-Acting Antivirals (DAAs) |
| Purpose of Treatment | Eliminate Hepatitis C virus from the body |
| Common Medicines | Sofosbuvir, Ledipasvir, Daclatasvir, Velpatasvir, Glecaprevir, Pibrentasvir |
| Treatment Duration | Usually 8–12 weeks |
| Cure Rate | More than 95% with proper treatment |
| Treatment for Acute Hepatitis C | May clear on its own; antivirals used if virus persists |
| Treatment for Chronic Hepatitis C | DAAs are the standard and most effective option |
| Genotype-Based Therapy | Treatment choice may depend on HCV genotype |
| Monitoring During Treatment | Regular blood tests to check viral load and liver function |
| Treatment in Liver Cirrhosis | Longer duration or adjusted regimen may be needed |
| Side Effects | Mild (fatigue, headache, nausea) |
| Hospitalization Required | Usually not required |
| Post-Treatment Follow-Up | Blood test after 12 weeks to confirm cure (SVR) |
| Lifestyle Support | Avoid alcohol, maintain healthy diet |
Direct-acting antiviral drugs (DAAs) can fix most instances of ongoing hepatitis C and intense hepatitis C. These are present-day prescriptions that the specialists supported in 2013. But unfortunately, the vast majority endure the medications, with the most widely recognized incidental effects being cerebral pain and weariness.
These drugs work by focusing on straightforward strides in the HCV life cycle to disturb the multiplication of viral cells.
DAAs to treat hepatitis C include:
- elbasvir/grazoprevir (Zepatier)
- glecaprevir and pibrentasvir (Mavyret)
- ledipasvir/sofosbuvir (Harvoni)
- peginterferon alfa-2a (Pegasys)
- sofosbuvir (Sovaldi)
Before DAAs opened up, the therapy for persistent hepatitis C was extended and awkward, with not great fix rates. Today, fix rates are over 90%Trusted Source.
Notwithstanding, new drugs can be excessive. Most government and personal health care coverage physician-recommended drug plans will assist with giving an inclusion to these meds. Some medication organizations and different projects can help, as well.
Talk with medical services proficient for exhortation on paying for hepatitis C therapy.
Diagnosis and tests
Specialists can analyze hepatitis C utilizing blood tests:
To start with, the specialist plays out a straightforward blood test to search for hepatitis C antibodies in the blood. A positive test implies that the individual has had an openness to the infection. However, it doesn’t be guaranteed to demonstrate progressing disease.
If the immune response test is positive, the individual might have a subsequent blood test called a hepatitis C RNA test. It will check whether the infection is as yet present in the blood.
A third blood test, called a genotype test, can determine the kind of hepatitis C infection available.
Hepatitis C in country wise
Here is a country-wise overview of Hepatitis C prevalence and status, presented clearly in table form:
| Country / Region | Estimated Prevalence | Key Notes |
| Egypt | Very High (≈8–10%) | Historically highest prevalence; major national elimination program |
| Pakistan | High (≈4–6%) | One of the highest burdens globally |
| India | Moderate (≈0.5–1.5%) | Large population; regional variation |
| China | Moderate (≈1%) | Significant number due to population size |
| United States | Moderate (≈1%) | Higher risk in baby boomers and IV drug users |
| Russia | High (≈3–4%) | Injection drug use a major factor |
| Brazil | Low–Moderate (≈1%) | Improving diagnosis and treatment access |
| Japan | Moderate (≈1–2%) | Older population more affected |
| Italy | Moderate (≈1–2%) | Declining due to effective treatment |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | Moderate–High | Limited screening in some regions |
| Middle East (excluding Egypt) | Low–Moderate | Varies by country |
| Europe (Western) | Low (<1%) | Strong healthcare and screening programs |
| Australia | Low (<1%) | Good access to antiviral therapy |
| Canada | Low–Moderate (≈0.7%) | Higher prevalence in high-risk groups |
| Global Average | ~0.7–1% | Around 58 million people living with HCV |
CONCLUSION
In Article that the individual has had hepatitis C for quite a while, a specialist might prescribe further tests to search for liver harm, measure the seriousness of any current injury, and preclude different reasons for damage.
These tests, for the most part, include blood tests and ultrasound checks. In addition, specialists utilize a liver biopsy to take a little example of liver tissue when different tests don’t give sufficient data.
Also Read: Inhealthfitness.com