Diabetes diet – blood sugar or blood glucose levels are excessive. Glucose is brought about by the food you eat. The cells of your body desire glucose to make your body strong to synthesize a hormone known as insulin that allows the glucose to enter your cells.
In type 1 diabetes, the body is unable to produce insulin. Whereas in type 2 diabetes, insulin is not produced and processed well in the body. In the absence of insulin that is sufficient, glucose levels increase in your blood and lead to high blood glucose levels.
Table of Contents
Pre Diabetes Diet Sheet (NHS Guidelines)
Pre-diabetes is an indicator that the sugar level in blood is not within the normal range yet is already excessively high to be classified as normal. As NHS guidelines point out, the good news is that pre-diabetes is frequently reversible with the help of the proper diet, physical exercises, and appropriate weight control. A healthy and balanced diet is very important in managing the blood glucose and the prevention of type 2 diabetes.
The pre diabetes diet sheet is an NHS-style diet based on whole foods, amounting to portions, and constant energy supply to maintain the level of blood glucose even during the day.
What Is Pre-Diabetes?
Pre-diabetes is a condition that arises in your body when it is unable to effectively utilize insulin. Unless it is controlled, it may advance to type 2 diabetes. According to NHS recommendations, small and regular lifestyle adjustments, in particular, dietary ones should be used to minimize the risk and enhance overall health.
Important Tenets of an NHS Pre Diabetes Diet.
The NHS encourages the consumption of a well-balanced plate diet, which contains all the major food groups and limits the intake of sugar and refined carbohydrates.
1. Choose Low Glycaemic Index (GI) Foods.
Foods with low-GI lead to the slow release of glucose, and this means that blood sugar spikes are not formed. They include oats, whole grains, lentils and most of the vegetables.
2. Increase Fibre Intake
High fibre foods enhance rate of digestion and maintain blood sugar levels. Whole grains, skinless fruits, and vegetables, beans, pulses.
3. Reduce Free Sugars
Limit the intake of sugar drinks, sweets, cakes and junk food. NHS says that reading the label on the food must be done with keenness with a mind to detect the existence of the hidden sugars.
4. Control Portion Sizes
Healthy foods are also known to raise the level of sugar in the blood in large quantities. It may be supported with the help of smaller dishes and mindful eating.
5. Include Lean Protein
Protein is also discovered to cause over-stuffing as well as keeping the blood sugar level constant. Choose lean meat, fish, eggs and tofu and legumes.
Pre Diabetes Diet Sheet (NHS Style Table)
| Meal Time | Recommended Foods | Foods to Limit or Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Early Morning | Warm water, green tea, or herbal tea | Sugary tea or coffee |
| Breakfast | Porridge with oats, wholegrain toast, boiled eggs, fruit | White bread, pastries, sugary cereals |
| Mid-Morning Snack | Nuts, seeds, apple, pear, yogurt (unsweetened) | Biscuits, chocolate, packaged snacks |
| Lunch | Brown rice or whole wheat roti, vegetables, dal, grilled chicken or fish | White rice, fried foods, creamy gravies |
| Evening Snack | Roasted chana, sprouts, vegetable soup | Sugary drinks, fried snacks |
| Dinner | Steamed vegetables, lean protein, small portion of whole grains | Heavy meals, refined carbs |
| Late Night (if needed) | Warm milk (low-fat) | Desserts, ice cream |
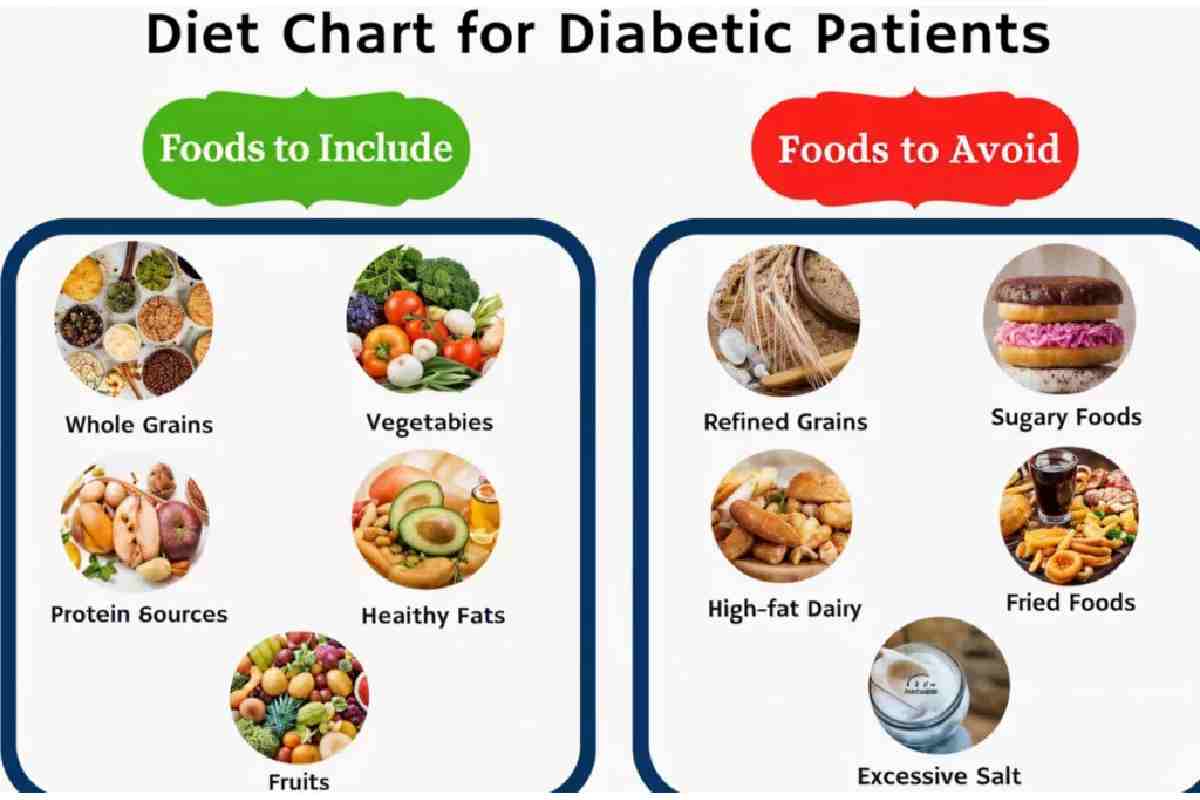
Foods Recommended by NHS for Pre-Diabetes
- Fibres (whole grains brown rice, oats, quinoa)
- Vegetables (spinach, broccoli, cauliflower) Non-starchy.
- Fruits (berries, apples, oranges – in moderation)
- Skim milk, or soy milk (symbols); low-fat yogurt, skim milk (symbols); skim ricotta cheese, skim mozzerella cheese (symbols).
- Fibres (green vegetables, white vegetables, nuts)
Foods to Limit or Avoid
- Fruity juices and sugar beverages.
- White bread, white rice and fined flour.
- Foods that are processed and packaged.
- Fried and fast foods
- Sweets, cakes, and desserts
Lifestyle Advice as well as Diet (NHS Advice)
Diet is best taken with healthy practices:
- Goal -150 minutes of moderate activity in one week.
- Have a normal body mass index.
- Sleep well and deal with stress.
- Smoking should be avoided and alcohol use should be minimised.
A pre diabetes diet sheet that is founded on the NHS guidelines can help a lot in lowering the chances of people being infected with type 2 diabetes. The trick is to be consistent, i.e. to eat whole, manage the number of portions, and limit sugar consumption every day. Sustainable, small-scale changes can become a significant contribution to a long-term health and blood sugar regulation.
With this moderate diet, you make a significant move into overturning pre-diabetes and enhancing an individual health condition.
Manage Diet in Diabetes Cases Effectively
- Have a balanced meal
- Consume specific amounts of healthy foods such as fresh veggies and fruits, whole grains, and ingredients low in fat contents.
- Eat foods which have considerably lower salty and fatty composition.
- Get at least half an hour of activity/exercise on a maximum of days of the week.
- Follow a workout routine.
- Quit smoking. If you don’t stop it voluntarily, find support from your family members and other nonsmokers to assist you.
- Check your feet each day for cuts, purple spots, blisters, and swelling. Alert your physician about any wounds that do not heal.
- Check your blood glucose using the approach your medical doctor tells you to.
How Do The Meals I Eat Affect My Blood Glucose Degrees?
Glucose that comes into your blood from certain foods is called carbohydrates, or” carbs.” Foods rich in carbs include delicacies, candies, tonics, viands, tortillas, and white rice. The more carbs you eat, the more advanced your blood glucose position.
If you’ve got type 1 or kind two diabetes, making the proper meal alternatives is a crucial way to keep your blood glucose at a position that gives fitness for you. If you manage your blood glucose, you decrease the risk of getting extreme health problems from diabetes, just like similar to vision loss and heart troubles. However, eating meals that preserve your blood glucose situation healthy may help type two diabetes later on If you have prediabetes or are at risk for diabetes.
What Is Type 1 Diabetes?
Category 1 diabetes, formerly juvenile diabetes or insulin-based diabetes, is an ordinary condition in this example; the pancreas makes little or no insulin. The body uses insulin to release sugar into cells to produce energy. Different factors like genetics and a few viruses may additionally motivate type 1 diabetes. Although type 1 diabetes diet typically appears during childhood or younger days, it can increase in Adults.
Indeed, after quite a few studies, type 1 diabetes has no treatment. Treatment is directed toward managing sugar within the blood, using insulin, implementing a weight loss program, and assisting with complications.
Symptoms:
Type 1 diabetes symptoms can appear suddenly and might consist of:
- Feeling extra thirsty than everyday
- Urinating plenty
- Bedwetting down in kids who’ve no manner to wet the bed in the course of the nighttime
- Feeling veritably empty
- Losing weight without attempting
- Feeling perverse or having other temper changes
- Feeling tired and susceptible
- Having a vague vision
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Diabetes is a circumstance because of the hassle of how the body regulates and makes use of sugar as energy That sugar is also called glucose—an extended-term result in excessive sugar circulating in the blood. Ultimately, sugar conditions can cause circulatory, frightened, and prone diseases. Diabetes there are mainly two troubles. The pancreas does not produce enough insulin — a hormone that controls the motion of sugar into the cells. Cells respond inadequately to insulin and soak up lower sugar.
Symptoms:
Diabetes frequently develops slowly. You can be dwelling with type 2 diabetes for years and not comprehend it. When signs are gifts, they’ll encompass:
- Increased thirst.
- Frequent urination.
- Increased hunger.
- Unintended weight reduction.
- Fatigue.
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores.
Ends
Diabetes is a slow killer, and not given a curable treatment. Still, its complications may be decreased through proper mindfulness and timely treatment. Three major complications are related to blindness, order damage, and heart attack. Keeping patients’ blood glucose levels under strict control is essential to avoid complications. One difficulty with tight control of glucose stages inside the blood is that such attempts might also result in hypoglycemia, creating more severe complications than increased blood glucose levels.
Also Read: Inhealthfitness.com